SECTION OUTLINE
- → Tissues in Human Body
- → Oral Cavity
- → Anatomy of Jaws
- → Human Dentition: Primary and Permanent Teeth
- → Periodontal Anatomy: Clinical and Histological Characteristics
- → Blood and Nerve Supply of Teeth and Associated Structures
- → Cranial Nerves: Trigeminal and Facial Nerve
- → Muscles of Mastication
- → Muscles of Facial Expressions
- → Occlusion and Malocclusion
- → Alveolar Process
INTRODUCTION
Cells are the smallest units of life. Cell is defined as the structural and functional unit of the living body. Clusters of cells are formed according to the comparable structure and function, which in turn leads to the formation of tissues in complex organisms. These tissues act as a unit and aid in various functioning of the organs which are essential to maintain biological life.
The current chapter sheds light on histology, the study of various tissues found in the human body along with its composition and function.
The structure of the cell contains (Fig. 1.1):
- Cell membrane
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm containing different organelles.
CLASSIFICATION OF TISSUES
The human body is made up of four basic types of tissues depending on their composition and function; namely epithelium, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues (Fig. 1.2).
The different function of each tissue is as follows:
- Epithelium: Lines and covers surfaces
- Connective tissue: Protects, supports, and binds together
- Muscular tissue: Produces movement
- Nervous tissue: Receive stimuli and conduct impulses.
EPITHELIUM
It forms the covering of surface of the body and aids in protection, adsorption, excretion, secretion, filtration, and sensory reception. However, it is important to consider the following points, which are as follows:
- Arrangement of epithelium is done to make one surface free and one surface attached, known as apical surface and basal surface, respectively
- Cells in epithelium are arranged either side by side or atop each other to form sheets of cells which in turn are held together by specialized junctions
- Basement membrane is formed by the attachment of epithelium to a layer of connective tissue at the basal surface. This adhesive layer is basically composed of secretions from the epithelial cells and the connective tissue cells
- However, cells of epithelium can be regenerated, if properly nourished.
Classification
Depending upon the basis of shape of the cells and the arrangement of the cells within the tissue, the epithelium is divided (Figs 1.3A and B). Generally, the arrangement of the cells is stated first, then the shape which is followed by epithelium to complete the naming, e.g. simple squamous epithelium.
According to the arrangement of the cells:
- Simple: Cells are found in a single layer attached to the basement membrane
- Stratified: Cells are found in two or more layers arranged atop each other
- Transitional: Cells are round in shape and can slide across one another to allow stretching.
According to the shape:
- Squamous: Flat, thin, scale-like cells
- Cuboidal: Cells have a basic cube shape in which the cell's height and width are about equal
- Columnar: Tall, rectangular or column-shaped cells which are basically taller in comparison to their width.
Distinguished Features
- Cilia (singular: cilium, Latin: eyelash): These are hair-like appendages which attaches to the apical surface of cells to produce movement
- Goblet cells: Specialized cells secrete mucus for lubrication and protect the surface of an organ
- Villi (singular: villus, Latin: shaggy hair): Some organ exhibits finger-like projections that arise from the epithelial layer to increase the surface area for faster and more efficient adsorption
- Microvilli: Small projections that arise from the cell's surface also help in enhancing surface area for absorption. Based on their bushy appearance, they are sometimes called as brush border of an organ.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium, single layer of flattened cells lines small air sacs of lungs called alveoli (Fig. 1.4A). One surface of epithelium faces an open space to the inside of the air sac, known as lumen and the cell surface facing it is the apical surface.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium lines kidney tubules and appears as dispersed thick-walled circular structures, when seen in the histological cross section (Fig. 1.4B).
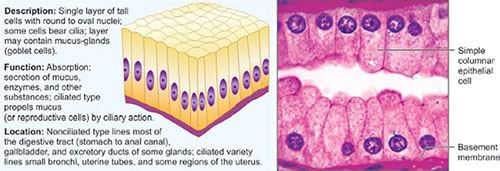
Simple Columnar Epithelium
The lining extends into the lumen and is usually seen as finger-like projections called villi. These villi aids in enhancing the absorption of the intestine by increasing the surface area. On cross section, along with large rectangular cells, clear-looking goblet cells are also found which secretes mucus for protection of the intestinal lining (Fig. 1.4C).
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
This type of epithelium is typified by irregularly shaped cells which mark the lining of trachea. The nuclei of the cells are seen scattered in different spots within the cells, which provide the tissue its false-layered appearance. In addition, it is covered with numerous tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which trap debris and dispense mucus secreted by the goblet cells across the surface of the tissue (Fig. 1.4D).
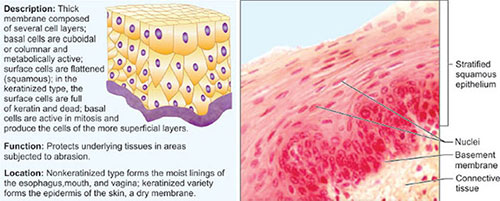
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Epidermis, the outer layer of skin constitutes multiple layers of flattened cells. However, these cells get flattened and subsequently die as the cells are pushed higher. The death of the cell is attributed to the depletion of nutrients from the sources present in the connective tissue. These, in turn, form the outer dead layers of the epidermis (Fig. 1.4E).7
Transitional Epithelium
This type of epithelium resembles a combination of cuboidal and columnar shaped cells. This is seen in the inner lining of the bladder in which tissue can stretch and distend without causing perforations in the wall lining (Fig. 1.4F).
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
It is the most extensively scattered tissue type present in the human body. It helps in protecting, supporting and binding together parts of the body.
The following section throws some light on the chief characteristics of connective tissue:
- Though connective tissue is extremely vascularized, some tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilages are less vascular in nature
- It is composed of various types of specialized cells
Classification
There are four types of connective tissues found in the human body (Fig. 1.5A):
- Connective tissue proper
- Loose connective tissue
- Areolar
- Adipose
- Reticular.
- Dense connective tissue
- Dense regular
- Dense irregular.
- Supporting connective tissue
- Cartilage
- Elastic
- Hyaline
- Fibrocartilage.
- Bone
- Fluid connective tissue
- Blood
- Lymph.
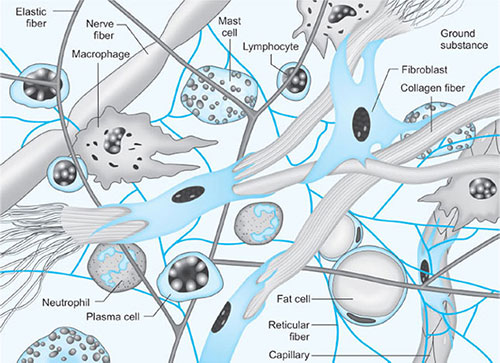
Areolar Tissue
It is a loose type of connective tissue which constitutes intermixing of fibers and cells. It shows a very diffuse arrangement (Fig. 1.5B). The cells appearing as dark spots within the tissue are known as fibroblasts (fibro: fiber, blast: to create).9
The prime function of these cells is to secrete the fibers. The larger fibers which appear pink in color and small black fibers are called collagen fibers and elastic fibers, respectively. Both these fibers and the rest of the substance collectively surround the cells, known as matrix.10
Adipose Tissue
These tissues present as large, irregular, bubble-like cells clustered together and scattered in a matrix alike areolar tissue (Fig. 1.5C). The cells are occupied with fat which acts as storage of energy, insulation, and protection.
Reticular Tissue
These fibers aid in supporting the cells of a soft internal skeleton like spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow (Fig. 1.5D).
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
This tissue is surrounded by the fibers and plays an important role of producing fibers. In addition, it also forms tendons and ligaments that are required to connect muscles to bones and bones to other bones (Fig. 1.5E).
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Dermis, the middle layer of the skin constitutes this type of tissue. Though composition is homogenous as of dense regular tissue, its constituents are not arranged appropriately as compared to dense regular tissue (Fig. 1.5F).11
Hyaline Cartilage
The lining below trachea is composed of rings of hyaline cartilage which are immersed in the organ in order to offer structure and support. The cartilage on cross section shows smooth, amorphous matrix containing collagen fibers with cells embedded within it. This matrix is produced by the cells known as chondrocytes which are contained within tiny chambers called lacunae or little lakes (Fig. 1.6).
Elastic Cartilage
The tissue that needs more stretching and maintenance of shape contains elastic fibers within the matrix of the tissue (Fig. 1.7). This type of tissue is present majorly in the structure of the external ear.
Fibrocartilage
Its arrangement is comparable to hyaline cartilage and forms the intervertebral discs in the spinal column, the pubic symphysis, and in the discs of the knee. It differs from hyaline cartilage in its rigidity, as it is less firm and exhibits more number of collagen fibers (Fig. 1.8).12
The cells found are also known as chondrocytes which are found in the lacunae.
Bone (Osseous) Tissue
Bone tissue is organized in concentric ring structures called osteons in center of which lies a Haversian canal (Fig. 1.9A). This canal contains blood vessels and provides nutrition to the cells within the tissue.
Moreover, this canal is surrounded by rings of bone tissue called lamellae which contain chambers as lacunae (Fig. 1.10). These lacunae in turn possess tiny channels called as canaliculi which permit the interaction of the cells with the blood supply. The cells embedded in the tissue are known as osteocytes (osteo: bone, cyte: cell).
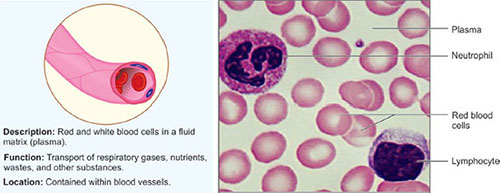
Blood
Blood is wrongly not considered as a tissue due to its liquid state, yet it fulfills all the requirements of being a connective tissue. It contains chiefly two types of cells; red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes).
In addition, tiny fragments of cells called platelets are also seen in this tissue (Fig. 1.11). Along with these cells, matrix also known as plasma is present which is made up of water, salts, gases, and proteins (nonliving materials).
Lymph
It is a thin opalescent fluid originating in organs and tissues of the body that circulates through the lymphatic vessels and is filtered by the lymph nodes. It fight infection, and in which are formed blood cells that is lymphocytes, monocytes, and plasma cells (Figs 1.12A and B).14
Lymphatic system is a vast, complex network of capillaries, thin vessels, ducts, nodes and organs that help to protect and maintain the internal fluid environment of the entire body.
THE INTEGUMENT
The skin or integument is the main organ which protects the body externally. Besides protection, it plays a vital role in providing insulation, temperature regulation and tactility (sense of touch). It also aids in the formation of vitamin D, essential for proper functioning of the body.
Composition
The skin is composed of three distinctive layers namely; epidermis, dermis and hypodermis.
Epidermis
It is the outer layer which is formed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, which is arranged into five layers called strata (singular: stratum), which are shown in Figs 1.13A and B)
- Stratum corneum, which is the outermost layer of flattened, dead cells
- Stratum lucidum, thin translucent layer present only in thick areas of the skin
- Stratum granulosum is named because of its richness of granules. The cells begin to die in the upper boundary of this layer
- Stratum spinosum is one of the thicker layers of dermis with potential of fast division of cells
- Stratum basale is the lowest layer of the skin which is attached to the dermis to form basement membrane. In this layer, cells continuously divide to create new cells.
Dermis
It is the middle layer and is formed from dense irregular connective tissue.
Dermal papillae, projections or ridges arise from the dermis and offer attachment points for the epidermis.
Hypodermis
It is the innermost or subcutaneous layer which is composed of adipose tissue.
Various Structures and Functions
The distinctive structures and functions of skin are as follows:
- Gland structures
- Eccrine gland: It secretes sweat which is the combination of water, salts, and urea and helps in cooling down the temperature of the body
- Sebaceous gland: It secretes sebum or oil which aids in keeping the skin soft and pliable.
- Nervous structures
- Free nerve endings: These are positioned near dermal papillae and are related with pain sensation
- Meissner's corpuscle: These touch receptors are positioned near dermal papillae and are associated with tactility
- Pacinian corpuscle: These pressure receptors are situated deep within dermis at the boundary of the dermis and hypodermis.
- Muscle structures
- Arrector pili: These are the muscle that pulls up hair follicle causing goose flesh or goose bumps.
- Appendages
- Hair shaft
- Hair follicle.
NERVOUS TISSUE
Neurons are the smallest functional units of the nervous system. Each neuron is composed of a cell body and two types of processes: axon and dendrites (Fig. 1.14). The function of the neurons is reflected in the number and types of processes arising from the cell body.16
Axon
It conducts impulses to other neurons or cells. Neurons have only one axon. The cell membranes of myelin cell predominantly contain fat which gives brain's white matter its fatty appearance.
Dendrite
It conducts impulses from synapse to the cell body. Depending on its function, a neuron may have multiple dendrites. Dendrites may undergo complex arborization to increase their surface area.